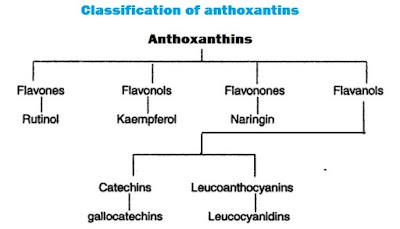
The anthoxanthins are glycosides which in boiling with dilute acid yield one or two molecules of monosaccharides and a flavones or a flavone derivative such as flavonal, flavanonal, or isoflavones.
The anthoxanthins are dissolved in the plant’s cell sap and are water soluble unlike the carotenoid which are fat-soluble. They contribute the cream or white color of cauliflower, onions, white potatoes and turnips.
Anthoxanthins turn an undesirable yellow color in alkaline water, and can even change to blue-black or red-brown under excessive heating or in the presence of iron or copper.
A short cooking time is desired for the anthoxanthins pigment. Otherwise, with prolonged heat, the pigment turns into an undesirable brownish gray color. In acid environment, anthoxanthins becomes lighter.
Anthoxanthins in vegetables
Flavonoids: Medicinal Properties and Synthesis
-
Flavonoids, characterized by the flavan nucleus, form a widely distributed
category of naturally occurring polyphenolic compounds found abundantly in
vario...